Investment Thesis: Mastercard

This issue's recommendation is one of the best companies from payment technology with a great innovating product and a global reach. We believe that it is an excellent choice for a long-term investment that can yield satisfactory returns.
This recommendation is just a start; the next step is to begin your due diligence process which will then help you make the investment decision. We strongly advise investors to do a thorough analysis of the recommendation and understand the soundness of the business before investing in this company. Also, please consult your investment advisor before making a decision
Business Profile (NYSE: MA)
Mastercard, Inc. is a technology company, which engages in the payments industry that connects consumers, financial institutions, merchants, governments, and businesses. It offers payment solutions for the development and implementation of credit, debit, prepaid, commercial, and payment programs. The company was founded in November 1966 and is headquartered in Purchase, NY.
Story
Mastercard is a leading global payment technology company, with a presence in over 210 countries and territories. This means that customers can use their Mastercard almost anywhere in the world. In the ever-growing world of digital payments, Mastercard has established itself as a prominent player alongside Visa. Mastercard is known for its innovation and has been at the forefront of developing new payment technologies, such as contactless payments, digital wallets, and biometric authentication. Mastercard is committed to providing secure payment solutions and has invested heavily in developing advanced security features to protect its customers' financial data. Mastercard has formed partnerships with a wide range of organizations, including banks, fintech companies, and merchants, to offer its customers a seamless payment experience. Mastercard is dedicated to providing excellent customer service and has a 24/7 customer service hotline, as well as an online portal where customers can easily manage their accounts and report any issues.
Business
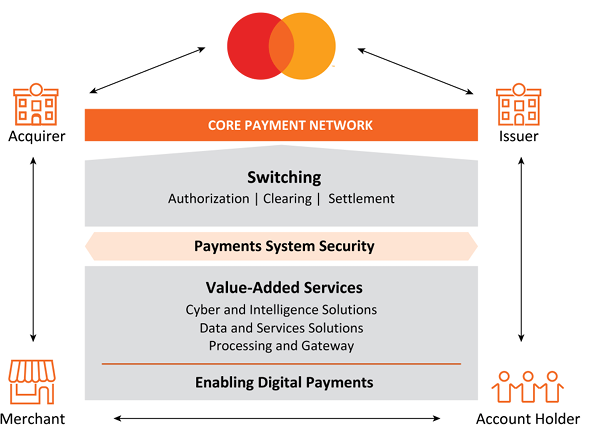
Let’s imagine you have a Mastercard credit card and you’re buying an item in a supermarket. The transaction will involve five parties: Mastercard; the cardholder (you); the merchant (the supermarket); an issuer (your bank that issued you the credit card); and an acquirer (the supermarket’s bank). The transaction process will then take place in six steps:
- Paying with your Mastercard credit card: You (cardholder) purchase your item from the supermarket (the merchant) with your credit card
- Payment authentication: The supermarket’s point-of-sale system captures your account information and sends it to the supermarket’s bank (the acquirer) in a secure manner.
- Submission of transaction: The supermarket’s bank gets Mastercard to request authorization from your bank (the issuer).
- Authorization request: Mastercard sends information of your transaction to your bank for authorization.
- Authorization response: Your bank authorizes your transaction and pings the go-ahead to the supermarket.
- Payment to merchant: Your bank sends the payment for your transaction to the supermarket’s bank, which then deposits the money into the supermarket’s bank account.
Mastercard’s revenue comes from the fees it earns when it connects acquirers and issuers which can be grouped into the following segments:
Domestic assessments are charges based on activity related to cards that carry the Company's brands where the merchant country and the country of issuance are the same. These assessments are primarily driven by the domestic dollar volume of activity (e.g., domestic purchase volume, domestic cash volume) or the number of cards issued.
Cross-border assessments are charges based on activity related to cards that carry the Company's brands where the merchant country and the country of issuance are different. These assessments are primarily driven by the cross-border dollar volume of activity (e.g., cross-border purchase volume, cross-border cash volume).
Transaction processing assessments are charges primarily driven by the number of switched transactions on our payment network. Switching activities include Authorization, the process by which a transaction is routed to the issuer for approval. Clearing, is the determination and exchange of financial transaction information between issuers and acquirers after a transaction has been successfully conducted at the point of interaction. Settlement, which facilitates the determination and exchange of funds between parties. These assessments can also include connectivity services and network access which are based on the volume of data transmitted and the number of authorization and settlement messages.
Other network assessments are charges for licensing, implementation, and other franchise fees.
Rebates and incentives These are payments that Mastercard pays to its customers.
Revenues from domestic assessments, cross-border volume fees, transaction processing, and other services collectively make up Mastercard’s gross revenue. We arrive at Mastercard’s net revenue when we subtract rebates and incentives from gross revenue.
With the ability to handle transactions in more than 150 currencies in over 210 countries, it should not surprise you to find that Mastercard has a strong international presence.
Financial Performance and Market Share
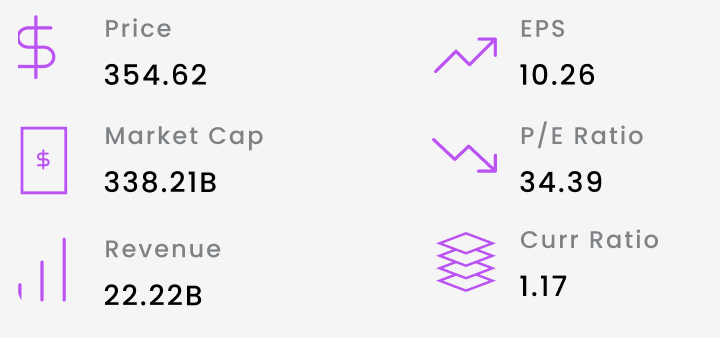
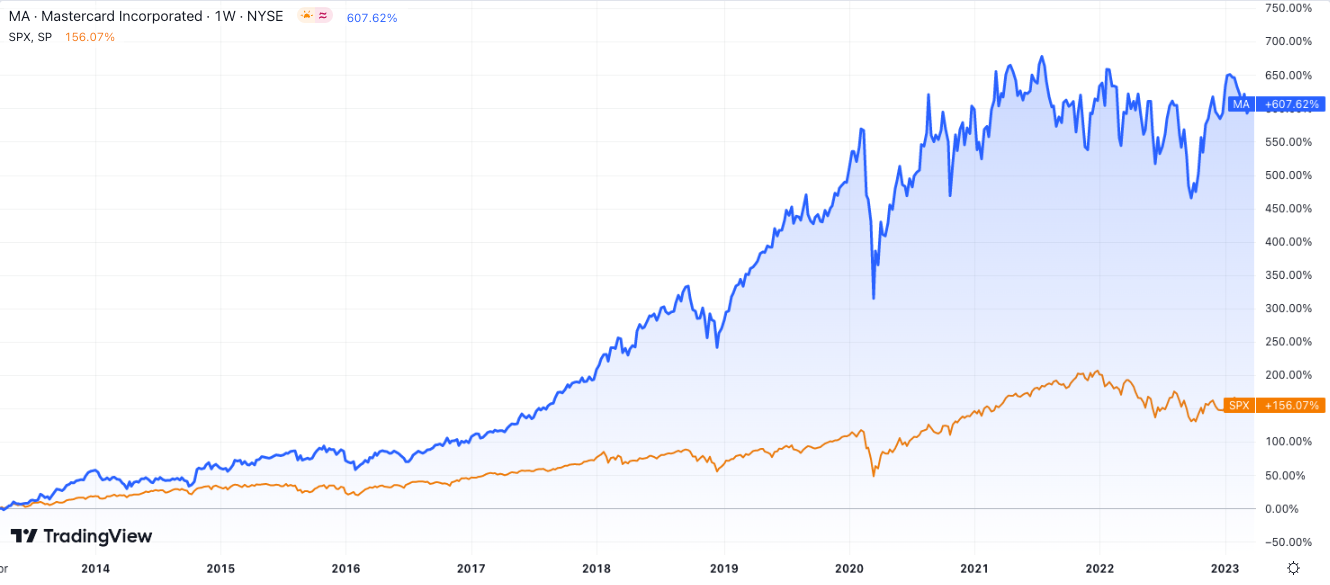
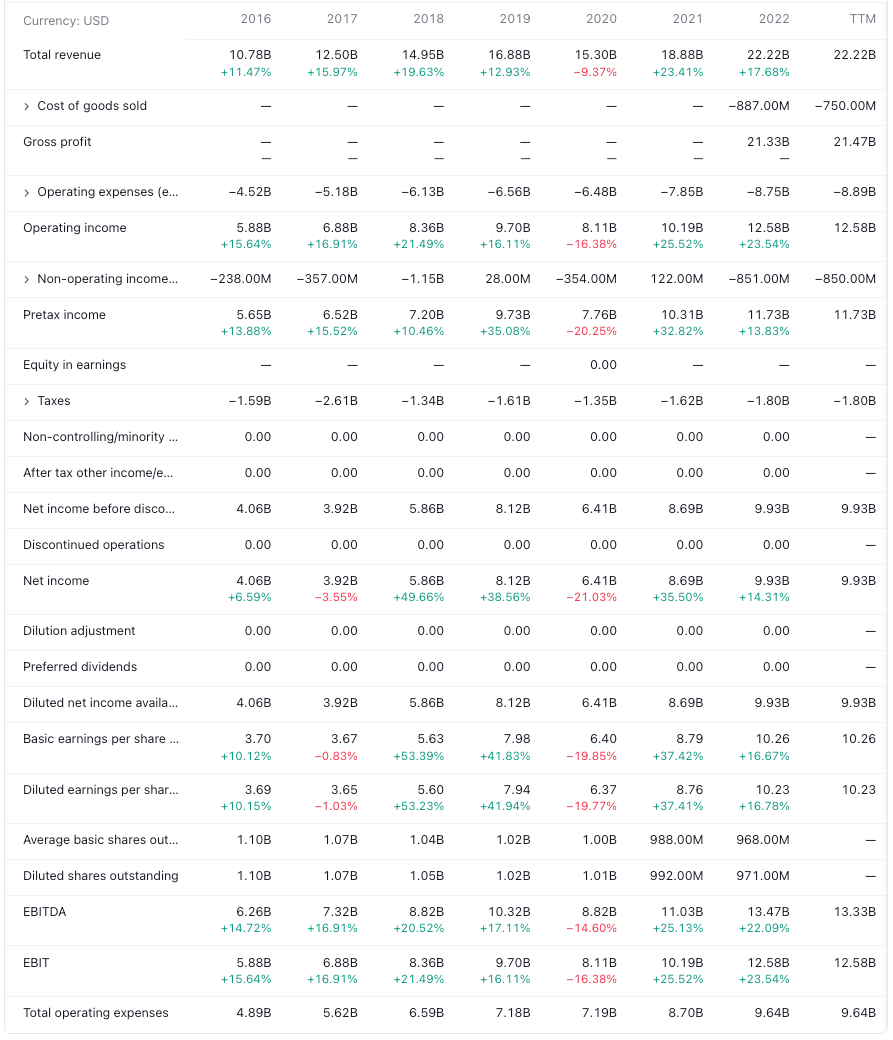
Mastercard has shown steady growth in recent years. As of 2022, the company reported net revenue of $22.2 billion, growing by 23% year over year. This growth in revenue reflects Mastercard's increasing market share in the digital payments space. Although Visa remains the market leader with a global market share of 61%, Mastercard is gradually closing the gap, capturing 39% of the market. Mastercard's financial performance over the past decade has been impressive. Over the past decade, the company's net revenue CAGR (compound annual growth rate) was 13.7%, while operating income CAGR stood at 12.3%. Mastercard's consistent growth and strong operating margins showcase the company's resilience and profitability.
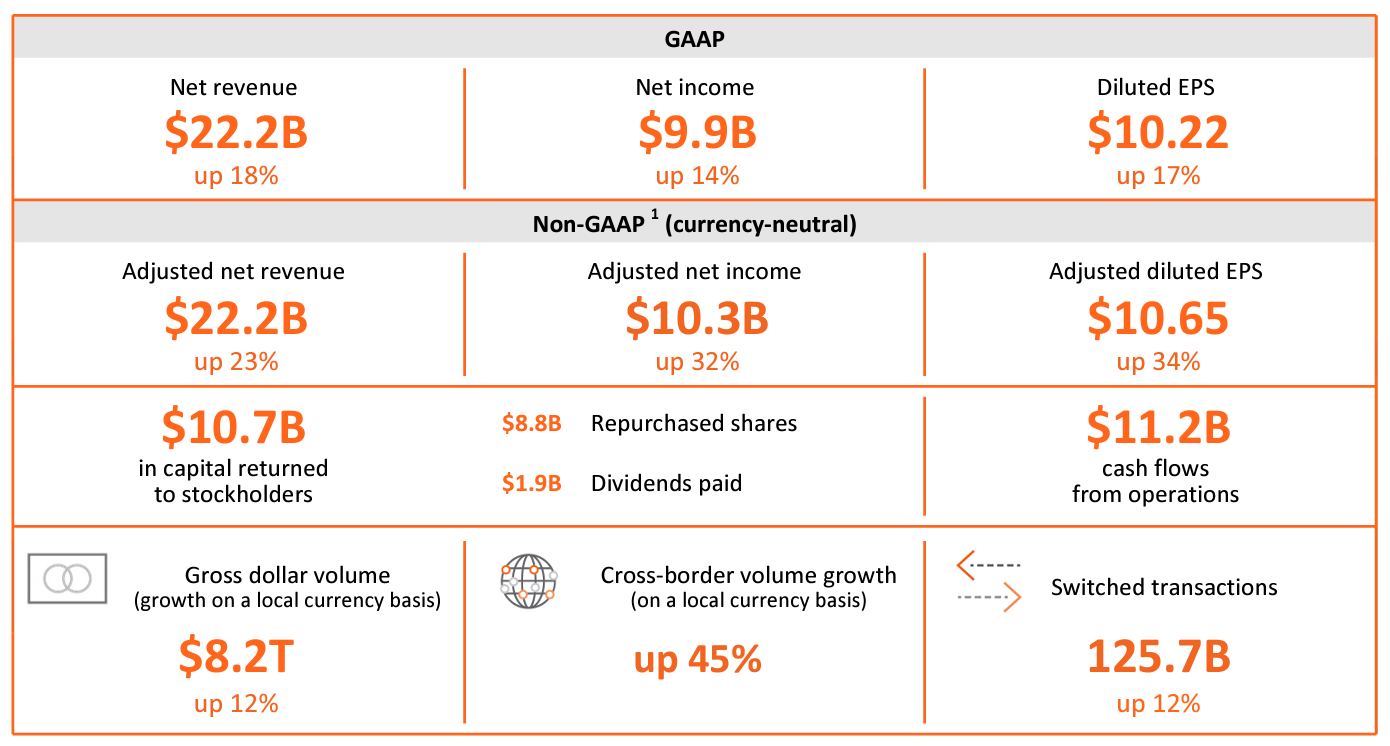
Visa has a greater presence in the market than Mastercard. However, when it comes to revenue per share, earnings per share, and revenue growth, Mastercard outperforms Visa. Mastercard could potentially offer greater profit in the long term due to its growth prospects.
Strong Business Model and Competitive Advantage
Mastercard operates as a payment processing network, connecting banks, merchants, and consumers to facilitate transactions. The company earns revenue through transaction fees, service fees, and data processing fees. Mastercard's competitive advantage lies in its strong brand recognition, global presence, and efficient network infrastructure. Mastercard's primary competitive advantage stems from its vast global payment network, which connects consumers, merchants, and financial institutions. The company benefits from the network effect, meaning that the value of its services increases as more users join the network. This allows the company to maintain a strong moat against potential competitors, ensuring continued growth and profitability.
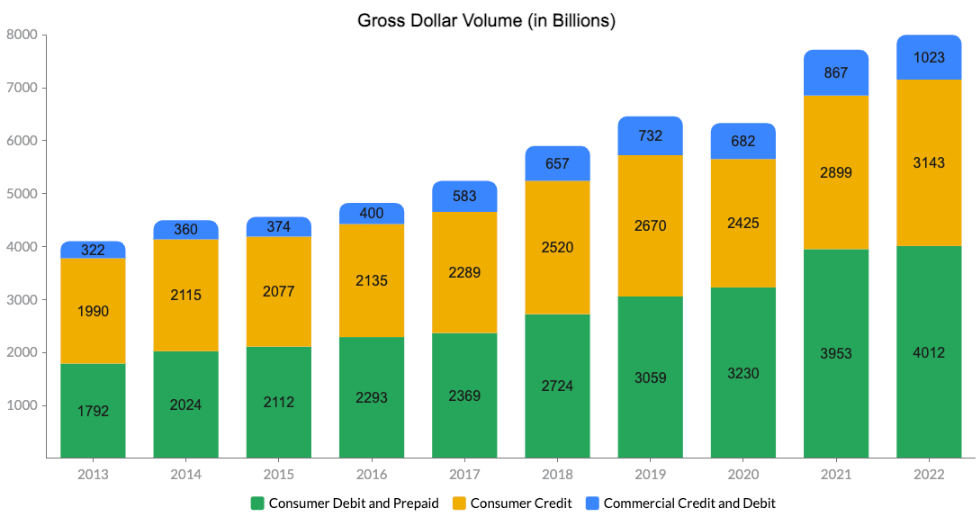
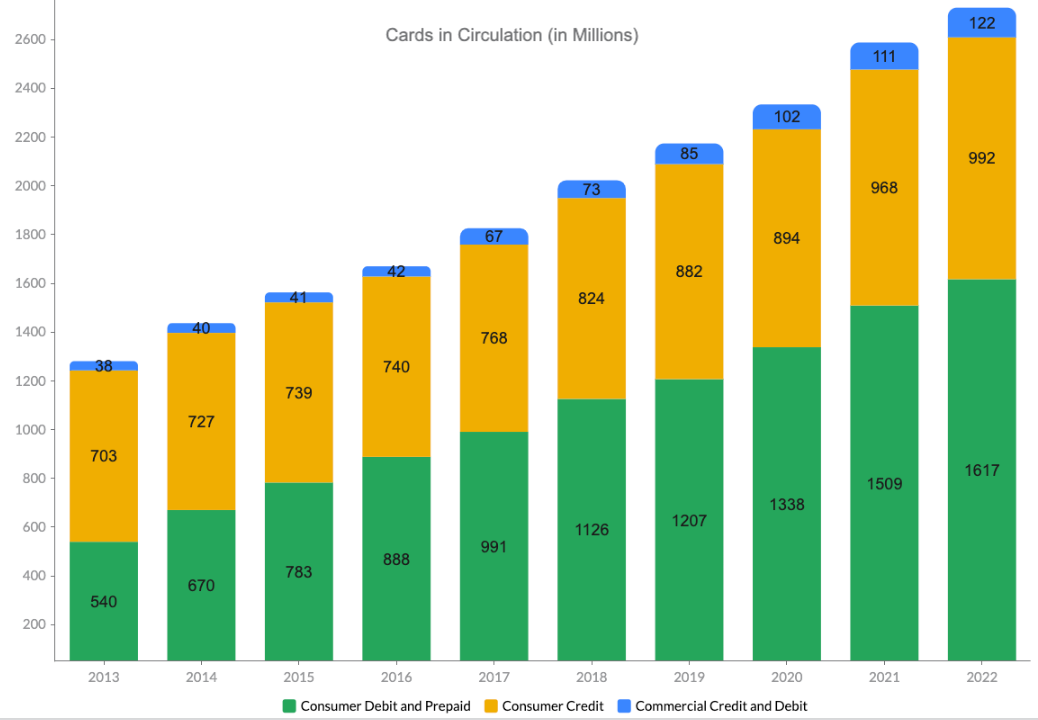
The competitive advantage is created by the network effects of having a base of 2.7B card members which can be used in 48M merchant locations in 210 countries and 150 currencies. Card-issuing banks basically have two network options to ensure global acceptance of their debit or credit cards: Mastercard and Visa. While American Express and Discover are doing a good job improving their own networks, they are still dramatically smaller than the big two. Mastercard and Visa have scale and know-how-based advantages.
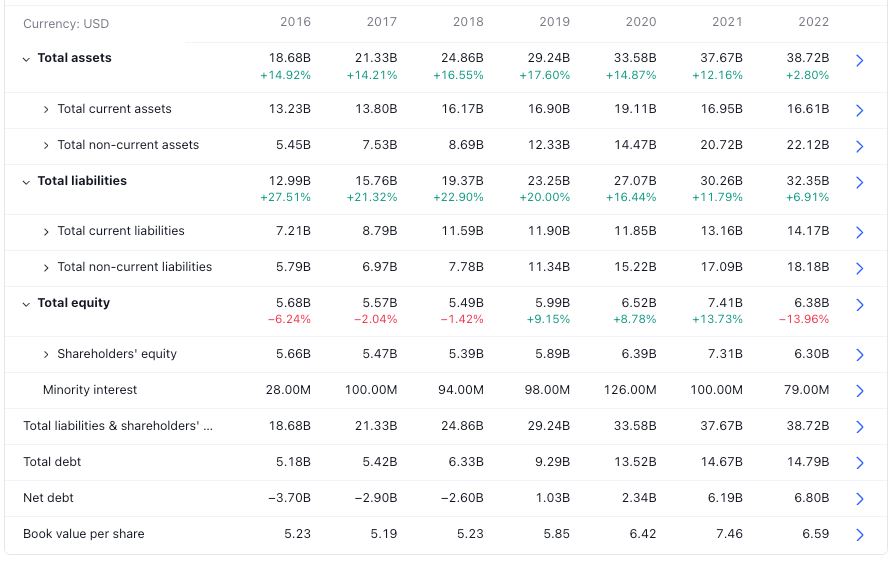
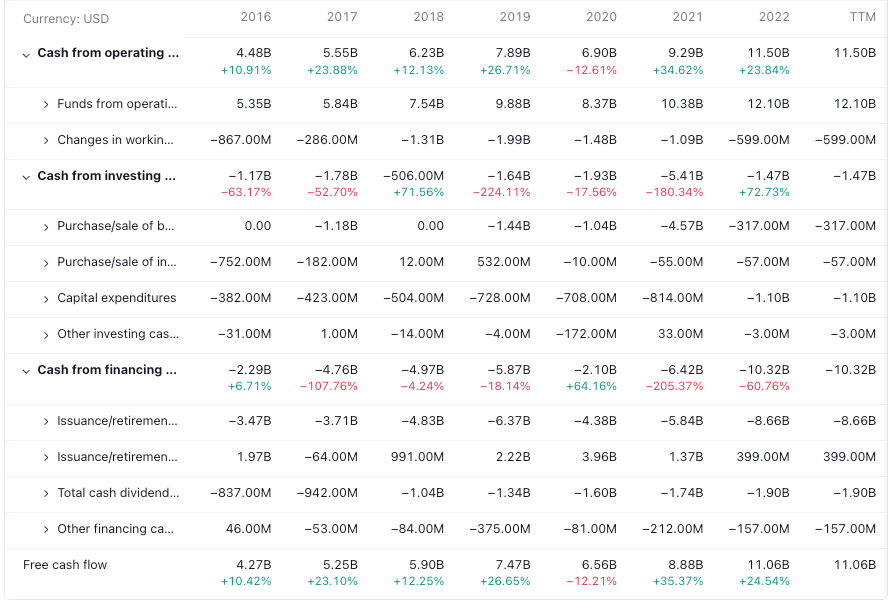
Mastercard's cash on hand for 2022 was $7.997B, and it was $8.48B & $11.182B in 2021 and 2020 respectively. Mastercard's long-term debt for 2022 was $13.749B, and it was $13.109B & $12.023B in 2021 and 2020 respectively. Mastercard has a strong balance sheet compared to cash on hand and long term debt. it shows that Mastercard has an excellent track record in generating free cash flow.
Partnerships and Acquisitions
Mastercard's growth strategy includes forging partnerships and acquiring fintech companies to enhance its product offerings and expand its reach. The company has partnered with several global tech giants like Google, Apple, and Samsung to enable digital wallet solutions. In addition, Mastercard has made strategic acquisitions, such as the purchase of Vocalink and Ekata, to strengthen its position in the payments ecosystem. Mastercard's recent partnership with Dynamic Yield, a leading personalization platform, aims to redefine customer engagement by integrating Mastercard's payment processing capabilities with Dynamic Yield's personalization technology. Element, the product of Mastercard's collaboration with Dynamic Yield, is designed to help businesses deliver personalized experiences for customers through various digital touch points. The platform combines Dynamic Yield's personalization technology with Mastercard's vast transactional data, enabling businesses to tailor their marketing efforts and product recommendations based on individual customer preferences and behavior. Mastercard's collaboration with Dynamic Yield paves the way for growth and value creation
Growth
There are several growth drivers that can propel Mastercard's performance in the coming years
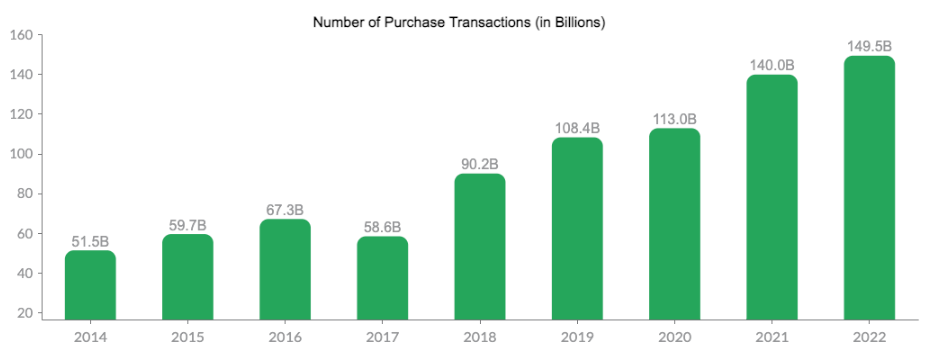
Global Digital Payments Expansion: As the world increasingly embraces digital payments, Mastercard stands to benefit from this trend. The shift from cash to digital transactions, especially in emerging markets, presents a significant growth opportunity.
Mastercard has been focusing on expanding its footprint in emerging markets, particularly in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. These regions represent a significant growth opportunity due to their large unbanked populations and increasing adoption of digital payments. The company has also been investing in digital solutions, such as contactless payments, digital wallets, and virtual cards, catering to the evolving needs of consumers.
Digital payments are expected to continue to rise in the next years but different markets are expected to lead the growth than in the last 5-6 years. Multiple forces have led to the growth of the global digital payment industry in the past years, such as an increased shift away from cash transactions and a growing reliance on smartphones. Moreover, mass internet usage has helped to drive forward the global e-commerce sector during the pandemic. The digital payment market worldwide was valued at $89.5 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach approximately $374.9 billion by 2030, a CAGR of 17.25% between 2022 to 2030.
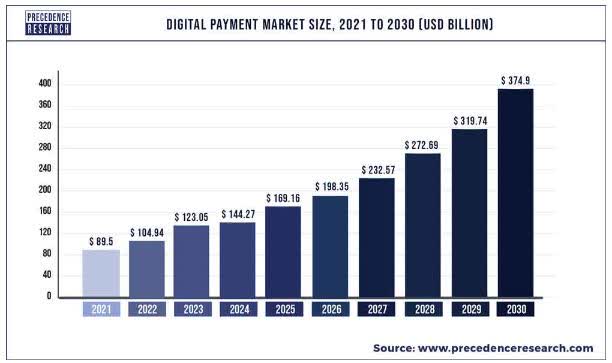
Emerging markets are starting to adopt digital payments rapidly. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the highest growth contributor to the digital payment market in the upcoming years. China is a huge market, but neither Visa nor Mastercard could capitalize on it just yet however India could be the key to growth for the two major credit card companies. Key government initiatives and policies in India are about to help to grow their market share and transaction volumes. The government of India is actively working on its strategy to digitize the economy and financial sector with the help of the two American giants.
India: There is no denying that Visa and Mastercard have almost total control over the credit card market in India, with an estimated 95% of all credit cards being issued by them however the credit card market is much smaller than the debit card market. India has about 77 million active credit cards compared to an astonishing figure of 940 million debit cards. Approximately 75% of these cards are powered by RuPay. The main disadvantage for MA and V was surprisingly not the number of cards they provide but the accessibility of the payment system [UPI].
The Unified Payment Interface or UPI, India's mobile bank-to-bank payments solution, has become immensely popular since its commencement in 2016. It has driven the growth of digital payments in India significantly and continues to be the go-to payment option for many. Via UPI mobile payments to the merchants, there are approximately 4 billion smartphone-based transactions per month. The approximately 100 million point-of-sales transactions by credit cards seem insignificant because there are only 7.3 million point-of-sale terminals for physical cards in India. Up until now, only debit cards and select credit cards powered by RuPay could have used the UPI. According to reports, the Reserve Bank of India is in the process of formulating plans to integrate Visa and Mastercard credit cards with the UPI. Joining the UPI system would be a significant opportunity for Visa and Mastercard. Through the UPI, they would get access to an extensive network of 230 million QR codes which stores utilize to receive payments. This could be a huge boost to both Visa and Mastercard and they could exponentially grow their operations in India and eventually their revenues.
China: In February 2020, Mastercard and NetsUnion JV were approved to Prepare for Domestic Operations in China. Mastercard announced that it has received in-principle approval from the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) to begin formal preparations to set up a domestic bankcard clearing institution in China.The application was submitted by Mastercard NUCC Information Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd, a joint venture of Mastercard and NetsUnion Clearing Corporation (NUCC). China is a vital market and the company has reiterated our unwavering commitment to helping drive a safer, more inclusive, and seamless payments ecosystem for Chinese consumers and businesses. The strategic collaboration between Mastercard and NUCC is founded on mutual synergies and will drive a simple, safe, and smart payments experience in a market well regarded as being one of the global frontrunners in digital payments technology. Even without China, Mastercard has ample room for growth. If the China opportunity works out then it would be icing on the cake.
E-commerce Growth: The rapid expansion of e-commerce globally creates a larger market for digital payment solutions. As more businesses and consumers adopt online shopping, Mastercard's services will become increasingly vital.
Contactless Payments: The demand for contactless payment options has accelerated due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Mastercard's investment in contactless payment technologies positions the company well to capitalize on this growing market.
B2B Payments: Mastercard has been focusing on expanding its presence in the B2B payment space, which represents a $120 trillion market opportunity. The company's acquisition of businesses like Nets and Transfast can help it gain a foothold in this lucrative segment.
Mastercard's initiatives to promote financial inclusion, such as its goal to bring 1 billion people into the financial system by 2025, contribute positively to the global community.
Innovation
Over the past decade, Mastercard has introduced numerous innovations that have transformed the payments industry and expanded the company's product offerings. Here are some of the most notable innovations from Mastercard in the past 10 years:
Mastercard Send: Launched in 2015, Mastercard Send is a global push payments platform that enables businesses, governments, and consumers to send and receive funds quickly and securely. The platform supports various use cases, such as person-to-person (P2P) transfers, business-to-business (B2B) payments, and cross-border remittances.
Tokenization: Mastercard introduced its tokenization service in 2013, which replaces sensitive card information with unique digital tokens during online and mobile transactions. This technology enhances the security of digital payments by reducing the risk of data breaches and fraud.
Mastercard Identity Check (formerly Mastercard SecureCode): Mastercard Identity Check is an authentication solution that leverages biometric technologies, such as fingerprint recognition and facial recognition, to provide a secure and seamless online shopping experience. Launched in 2016, this technology reduces the need for passwords and helps prevent unauthorized transactions.
Contactless Payments: Mastercard has been at the forefront of promoting contactless payments, which allow consumers to make transactions by tapping their card or mobile device on a compatible point-of-sale terminal. Over the past decade, Mastercard has worked closely with merchants, banks, and governments to drive the adoption of contactless payments globally.
Mastercard Track: Launched in 2018, Mastercard Track is a suite of products and services designed to streamline B2B payments and enhance supply chain efficiency. Track includes solutions for business verification, data exchange, and payment management, aiming to simplify complex B2B transactions and improve cash flow management.
Mastercard QR: Introduced in 2016, Mastercard QR is a mobile-based payment solution that enables consumers to make purchases by scanning a QR code at the point of sale. This technology has been particularly successful in emerging markets, where it helps drive financial inclusion by enabling merchants to accept digital payments without investing in expensive infrastructure.
Mastercard Blockchain: In 2017, Mastercard unveiled its proprietary blockchain technology, designed to support secure and transparent transactions for various use cases, such as cross-border payments, trade finance, and supply chain management.
Mastercard Labs: Mastercard Labs is the company's global research and development arm, responsible for fostering innovation and exploring emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G connectivity. Since its establishment in 2010, Mastercard Labs has played a crucial role in driving the company's innovation agenda and developing new products and services.
These innovations, among others, demonstrate Mastercard's commitment to staying at the forefront of the rapidly evolving payments industry and delivering cutting-edge solutions that enhance security, convenience, and efficiency for consumers, businesses, and governments worldwide.
Strong Leadership
Mastercard's leadership team is comprised of experienced professionals with diverse backgrounds in finance, technology, and business strategy. The company's executive team is responsible for driving innovation, expanding the company's global presence, and ensuring sustainable growth. Here are some key figures in Mastercard's leadership:
- Michael Miebach is the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Mastercard, having assumed the role in January 2021. Miebach has been with Mastercard since 2010, serving in various leadership positions, including Chief Product Officer and President of the Middle East and Africa region. Prior to joining Mastercard, he held positions at Barclays Bank and Citibank. Miebach's extensive experience in the payments industry and his deep understanding of Mastercard's business have positioned him to lead the company's continued growth and innovation.
- Sachin Mehra serves as the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) of Mastercard. He has been with the company since 2010, holding various leadership roles in finance, investor relations, and business planning. Before joining Mastercard, Mehra worked at General Motors in various finance-related positions. As CFO, Mehra is responsible for overseeing the company's financial strategies, capital allocation, and investor relations.
- Craig Vosburg is the chief product officer for Mastercard and a member of the company’s management committee. He leads an integrated product management and engineering organization, specifically designed to maximize the company’s customer-centric focus through an end-to-end approach to design and delivery. The team will innovate and scale the products and services that solve real-world problems and help shape the fabric of the modern global economy. He joined the company in 2006 and has held several leadership roles, including President of North America, Group Executive of U.S. Market Development, and Executive Vice President of Core Products.
- Michael Froman serves as vice chairman and president, Strategic Growth for Mastercard. In that role he is responsible for growing strategic partnerships, scaling new business opportunities and advancing the company’s efforts to partner with governments and other institutions to address major societal and economic issues. He and his team drive financial inclusion and inclusive growth efforts and work to develop new businesses key to the company’s strategic growth. Mike is chairman of the Mastercard Center for Inclusive Growth and is a member of the company’s management committee.
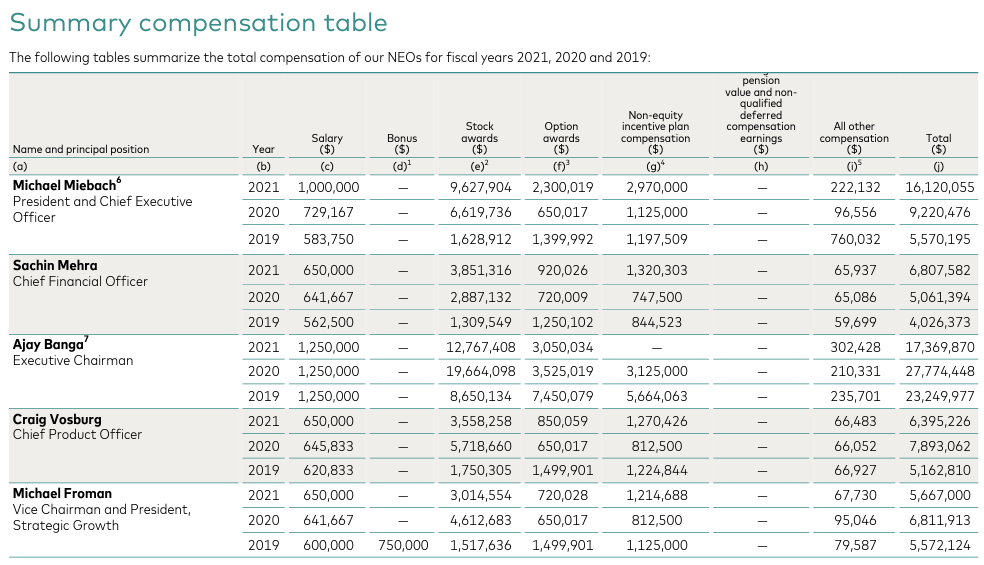
Mastercard has a very well-designed compensation scheme for executives to align with shareholder's interests. In 2021, 60% of CEO Michael Miebach's total compensation is from performance stock units (PSUs). PSUs would be tied to performance against three-year adjusted net revenue and adjusted EPS growth goals and modified by Mastercard’s relative Total Shareholder Return (TSR) performance against S&P 500 companies. The majority of the total compensation of Mastercard’s other key leaders also came from PSUs and stock options. Mastercard’s other key leaders were mostly promoted to their current roles after spending years with the company. The fact that Mastercard regularly promotes from within is another positive sign of the company’s culture.
Risk
While Mastercard's growth prospects appear promising and the odds are in the company's favor, there are risks and challenges to consider. These include:
Regulatory Risk: Payment processors operate in a highly regulated environment, and changes in regulations can impact Mastercard's business. For instance, interchange fee regulations can directly affect the company's revenues.
Competition: Intense competition in the payment processing industry from established players like Visa and emerging fintech companies may challenge Mastercard's growth trajectory.
Cybersecurity: As a digital payment provider, Mastercard faces potential cybersecurity threats that could damage its reputation and operations.
Recessions: With the current macro economic condition, there is a potential economic downturn in the near future, and payment activity on Mastercard's network could decrease, affecting its business performance. It may lead to painful share price declines if the company experiences growth hiccups, even if temporary. Long-term investors should be comfortable with this risk.
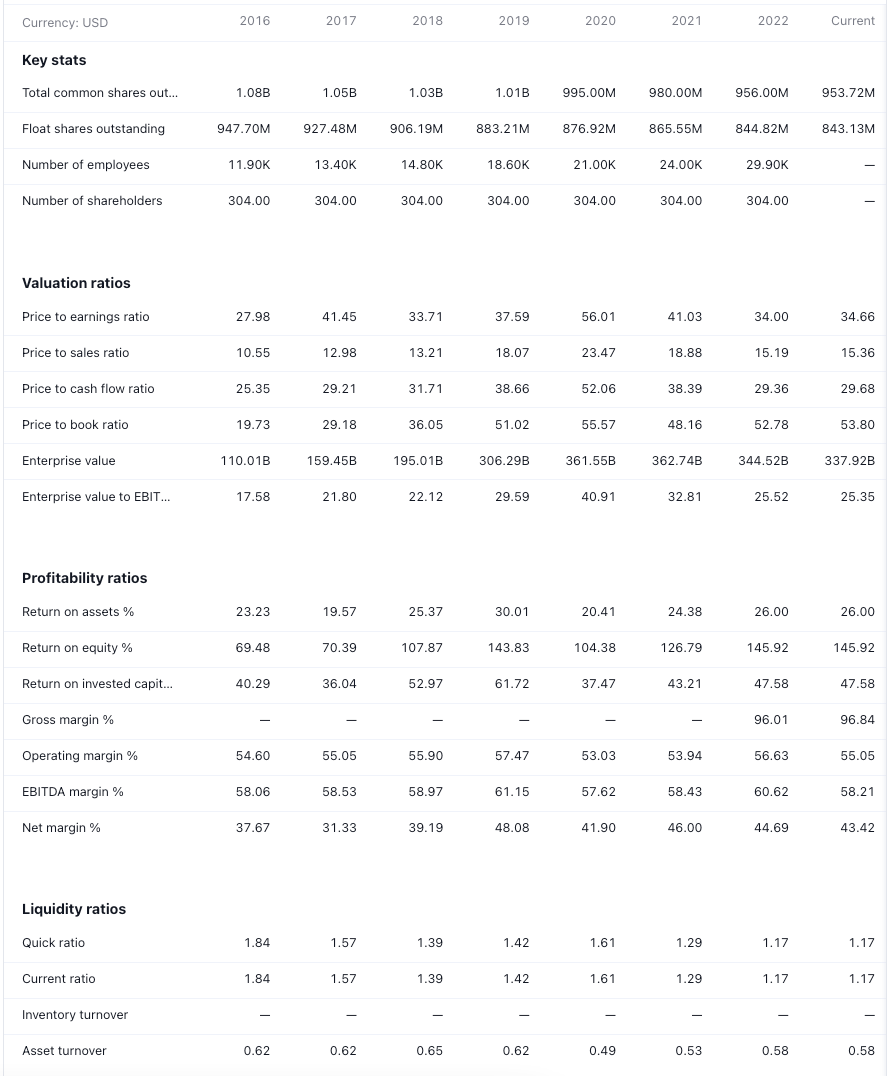
The following data snapshots are as of 03/27/2023 from tradingview website
Key Stats
Performance
Financial Statements
Income Statement
Balance Sheet
Cashflow
Statistics
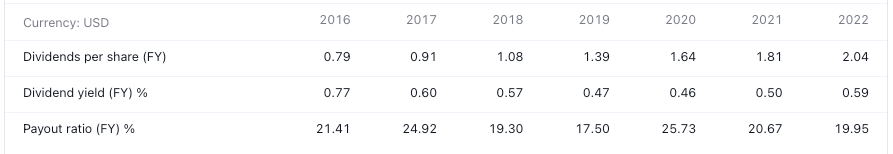
Dividends
Sources: Mastercard Investor Relations, Mastercard Newsroom, Statista, WallStreetZen, Seeking Alpha, Value Investor Club, Compounder Fund, Yahoo Finance, Fool, Nasdaq
Unlock the power of compounding
We are changing the way that people build wealth. If your portfolio is performing below S&P 500 in the last 5 years, then you need to subscribe here. Discover remarkable stories directly to your inbox. As a subscriber, you'll receive the valuable recommendation of an exceptionally outstanding company that are designed to help you build wealth.
Gain access to exclusive benefits by subscribing today!






Disclaimer: Please note that this newsletter is a financial information publisher and not an
investment advisor. Subscribers should not view this newsletter as offering personalized legal or investment
counseling. Investors should consult with their investment advisor and review the prospectus or financial / stock
recommendation of the issuer in question before making any investment decisions. All articles, blogs, comments,
emails, and chatroom contributions - even those including the word "recommendation" - should never be construed as
official business recommendations or advice. Liability of all investment decisions resides with the individual
investor.
Snowball Investing does not provide any guarantees, warranties, or representations, whether explicitly or
implicitly, regarding the accuracy, reliability, completeness, or reasonableness of the information presented. The
opinions, assumptions, and estimates expressed represent the author's viewpoints as of the publication date and are
subject to modification without prior notification. Projections made within the document are based on various market
condition assumptions, and there is no assurance that the anticipated results will be attained. Snowball Investing
disclaims any responsibility for losses incurred due to reliance on this document's content. It is important to note
that Snowball Investing is not offering financial, legal, accounting, tax, or other professional advice, nor is it
assuming a fiduciary role.




Member discussion